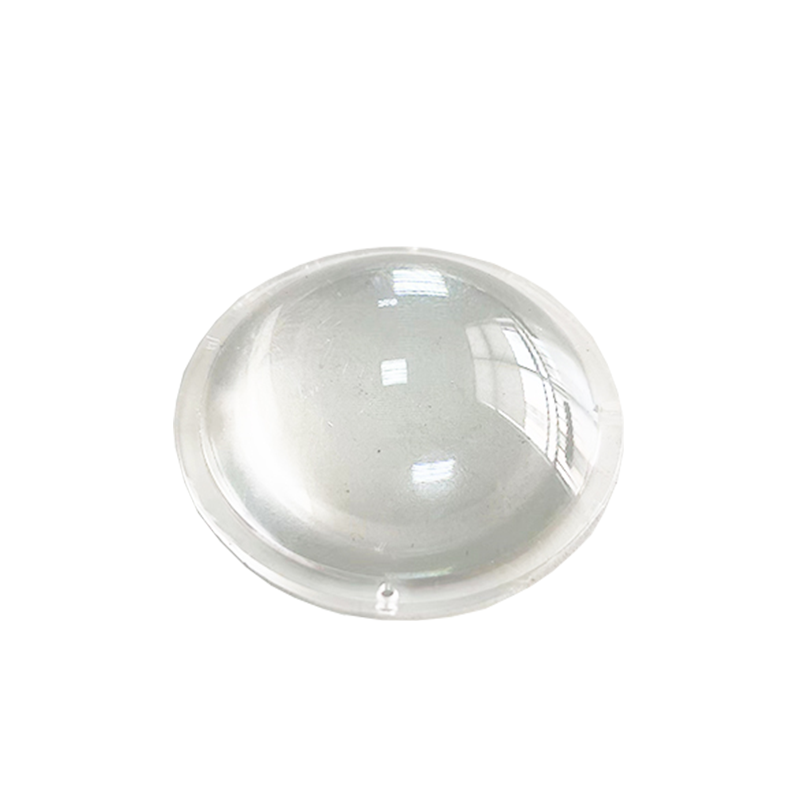
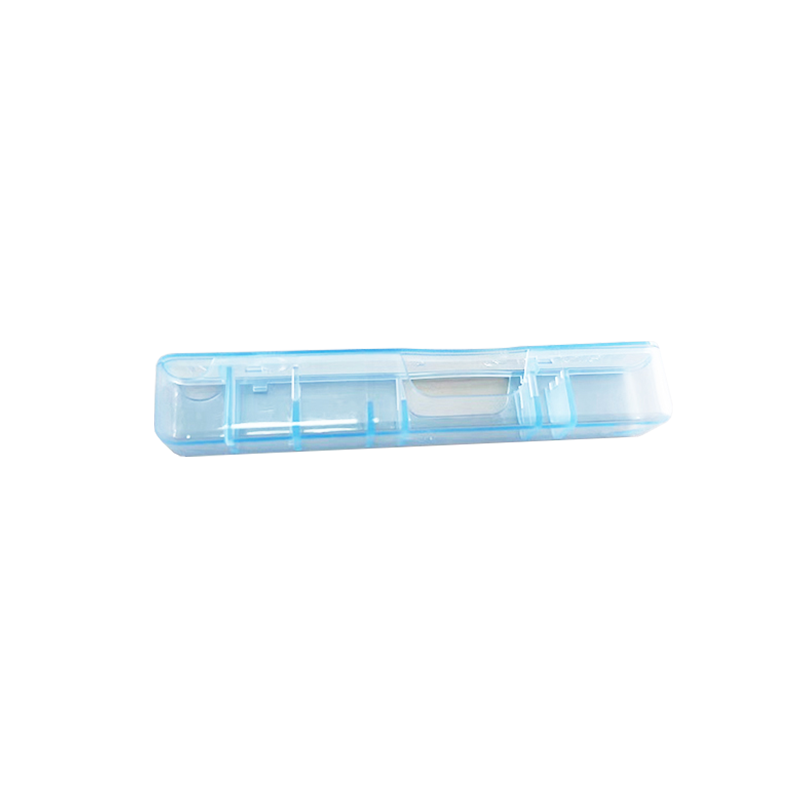
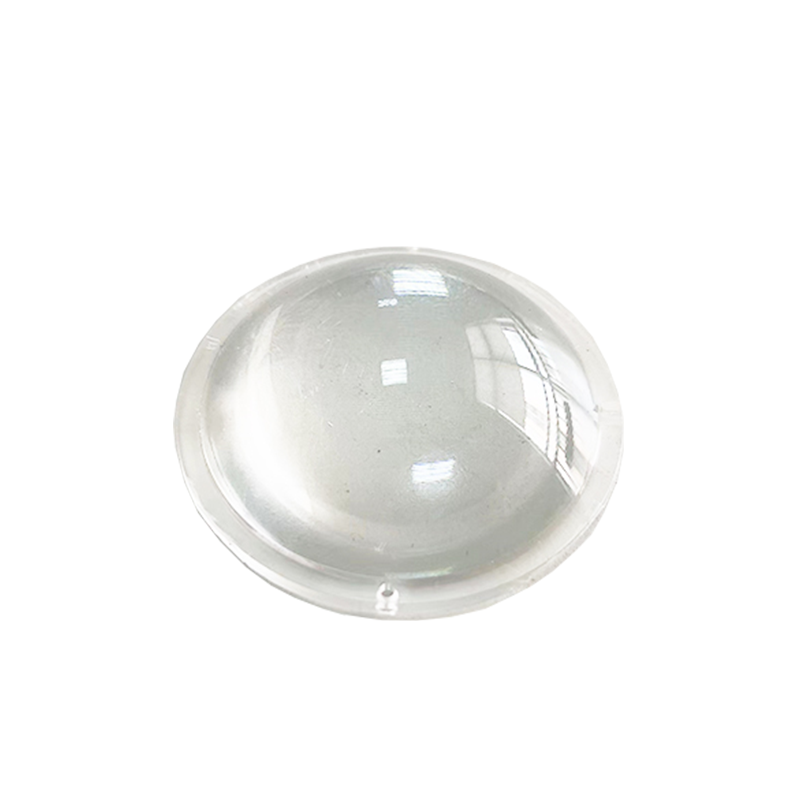
Medical Plastic Case
- Changshu Eternal Prosperity
- Jiangsu
Product parameters:
Colors can be customized; The shape can be customized; Materials can be customized; Support custom drawings.
Minimum order quantity: No minimum order quantity
Product parameters:
Colors can be customized; The shape can be customized; Materials can be customized; Support custom drawings.

Minimum order quantity:
No minimum order quantity
Company Introduction:
The company is located in the northeast of Changshu City, with Shanghai to the east, Suzhou to the south, Wuxi to the west, and the Yangtze River to the north. It is 10 kilometers away from Changshu Port and is a technology-based enterprise specializing in mold design, manufacturing, and plastic product production.
Product quality control:
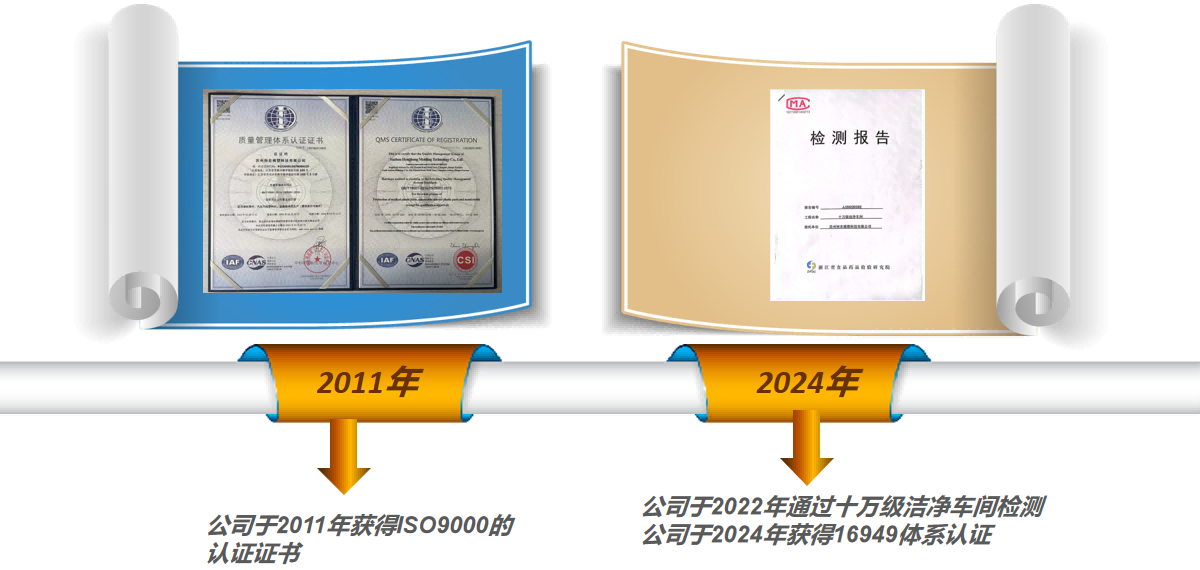
The company has ISO9000 quality management system certification; The raw materials for each product are sourced from high-quality imported or wholly-owned factories, ensuring customers can use them with peace of mind.
Enterprise personnel management philosophy:
Actively create a harmonious, united, mutually supportive, and upward environment that can unleash the maximum creativity of each employee.
Application industries:
Automotive accessories and medical devices, as a dual track with high growth potential and high barriers, have always been known as the "golden track" of the capital market.
FAQ
Detailed explanation of the production process of medical plastic products
The production of medical plastic products needs to meet special requirements such as high cleanliness, biocompatibility, and sterilization resistance. The core process includes material selection, molding processing, post-treatment, and sterilization. The following are the main production processes and technical points:
1. Material selection and pretreatment
Medical plastics must comply with regulatory requirements such as ISO 10993 (biocompatibility standard) and USP Class VI (United States Pharmacopeia). Common materials include:
Polypropylene (PP): syringes, infusion bottles
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC): infusion tubing (requires the use of non-toxic plasticizers)
Polycarbonate (PC): Transparent surgical instruments
Polyurethane (PU): Artificial blood vessels, catheters
Degradable plastics (PLA/PGA): sutures, absorbable scaffolds
Pre treatment process:
Drying: Some materials (such as PET, PC) need to be dried to remove moisture and avoid the formation of bubbles during molding.
Blending modification: adding stabilizers, antibacterial agents, etc. to enhance performance.
2. Molding process
According to the shape and purpose of the product, medical plastic products mainly use the following molding techniques:
(1) Injection Molding
Applicable products: syringes, test tube plugs, surgical instrument handles
Key points of the process:
High precision molds ensure dimensional stability (such as micrometer level tolerances for syringes).
Cleanroom (ISO level 8 or higher) to prevent contamination.
(2) Extrusion molding
Applicable products: infusion tubes, catheters, medical films
Key points of the process:
Using medical grade screws and barrels to avoid heavy metal precipitation.
Online detection of thickness and surface defects (such as laser calipers).
(3) Blow Molding
Applicable products: medicine bottles, eye drops bottles
Key points of the process:
Multi layer co extrusion technology (such as PP/EVOH/PP) enhances barrier properties and extends the shelf life of drugs.
(4) Thermoforming
Applicable products: Blister packaging (such as surgical instrument trays)
Key points of the process:
The material needs to be resistant to ethylene oxide (EO) or radiation sterilization.
(5) 3D printing (Additive Manufacturing)
Applicable products: Personalized implants (such as skull repair patches), surgical guides
Materials: PEEK, TPU, UV curable resin (requires biocompatibility certification).
3. Special Process Cases
(1) Multi layer co extrusion of conduits
Structure: Inner layer (lubricating PU)+middle layer (reinforced nylon)+outer layer (wear-resistant PE).
Process: Precision extrusion+laser drilling (such as dialysis catheter side holes).
(2) Laser cutting of biodegradable scaffolds
Material: Polylactic acid (PLA) or magnesium alloy.
Process: Laser precision cutting followed by electrolytic polishing to avoid scratching blood vessels.
5. Industry Trends and Challenges
Trend:
Green materials: bio based plastics (such as sugarcane PE) replace petroleum based products.
Intelligent production: AI quality inspection reduces defect rates.
Challenge:
Sterilization compatibility (such as the impact of irradiation on material properties).
Recycling difficulties (plastics contaminated with medical waste require special treatment).














