Medical Plastic Accessories
- Changshu Eternal Prosperity
- Jiangsu
Our company sells medical plastic accessories;
The company obtained ISO9000 certification in 2011;
Passed the 100000 level clean room inspection in 2022;
Obtained 16949 system certification in 2024.
Product parameters:
Colors can be customized; The shape can be customized; Materials can be customized; Support customized drawings
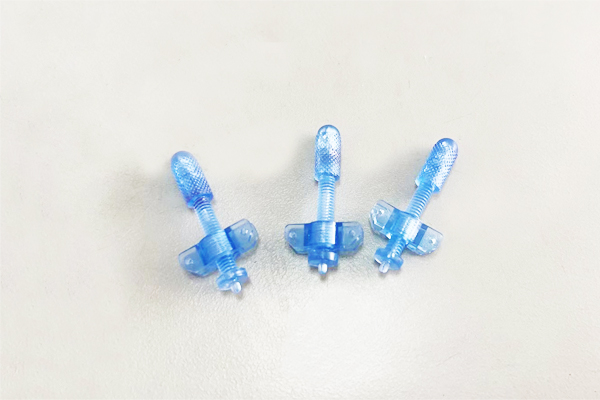

Medical plastic products
Our company is a Chinese enterprise specializing in the research and production of plastic products for minimally invasive surgical medical equipment and ophthalmic surgical medical equipment. Selling customized medical plastic accessories.
Enterprise advantages:
1. Continuously enriching the product line, focusing on automotive interior parts, medical devices and other fields, with an annual production capacity increased to 3 million sets;
2. The production equipment includes 3 CNC machining centers, 3 Beijing precision carving centers, 4 wire cutting centers, and mold making equipment such as lathes, milling machines, grinders, and electric discharge machines. We also provide 16 injection molding processing equipment for 50-800 tons.

FAQ
Performance degradation and safety hazards of medical plastic products during use
Medical plastic products play an indispensable role in medical practice, from disposable syringes and infusion tubes to plastic components of surgical instruments. The stability of their performance directly affects medical safety. However, during use, these plastic products are often affected by various factors, leading to performance degradation and a series of safety hazards, which require high attention from the medical industry.
1、 Main manifestations and causes of performance degradation
(1) Degradation of physical properties
The attenuation of physical properties is one of the most common problems in the use of medical plastic products. Taking disposable syringes as an example, their syringes and push rods are usually made of polypropylene, which may become brittle after long-term storage or repeated exposure to certain disinfectants. This is because when polypropylene is subjected to ultraviolet radiation, high temperature, or chemical reagents, its molecular chains will break, resulting in a decrease in material toughness and an increase in brittleness. When medical staff use fragile syringes for injection operations, it is very easy for the syringe to rupture, which not only causes waste of medication, but also may lead to scratches on medical staff, increasing the risk of infection.
The situation with infusion tubes is even more complex, as they are usually made of polyvinyl chloride and contain plasticizers inside to ensure their flexibility. But when in contact with fat soluble drugs (such as certain antibiotics, vitamins, etc.), plasticizers may be dissolved and precipitated by the drugs, causing the infusion tube to become hard, brittle, and significantly reduced in flexibility. This will make the infusion tube prone to breakage during use, affecting the normal flow of infusion. Meanwhile, the precipitation of plasticizers may also interact with drugs, altering their properties and efficacy.
(2) Changes in chemical properties
The change in chemical properties is also an important manifestation of the performance degradation of medical plastic products. Some medical plastic products may undergo chemical reactions when in contact with specific chemicals, resulting in a decrease in the chemical stability of the material. For example, plastic containers used to hold disinfectant solutions may dissolve or adsorb if their material does not match the chemical properties of the disinfectant solution. Some components in the container may dissolve into the disinfectant solution, contaminating the solution; The effective ingredients in disinfectant solutions may also be adsorbed by containers, reducing the disinfection effect and affecting the quality of medical disinfection.
For medical plastic components implanted in the body, such as plastic pads for artificial joints, they will be eroded by body fluids and rubbed by human tissues during long-term use in the body. Various chemical components in body fluids may undergo slow chemical reactions with plastics, leading to changes in their chemical structure and subsequently affecting their mechanical properties and biocompatibility. Over the long term, there may be component wear, aging, and even human rejection reactions.
(3) Decrease in mechanical properties
The decline in mechanical properties is mainly reflected in the strength, elasticity, and wear resistance of medical plastic products. Plastic hemostatic forceps, tweezers, and other instruments used in surgery may experience fatigue damage to their plastic components due to stress and temperature changes during repeated use and disinfection. For example, high temperature and high pressure sterilization can weaken the binding force between plastic molecules, resulting in a decrease in the strength of the instrument, which may cause breakage during surgical operations and affect the smooth progress of the surgery.
Plastic bandages used for wrapping and fixing will gradually lose their elasticity with prolonged use and repeated stretching. A bandage with decreased elasticity cannot provide sufficient pressure to the wound, affecting its healing and even leading to complications such as bleeding and swelling.
2、 Specific manifestations of safety hazards
(1) Patient health risks
Medical plastic products with performance degradation pose the most direct and serious health risks to patients. When the infusion tube ruptures due to performance degradation, it may cause air to enter the blood vessels, leading to air embolism, which can be life-threatening in severe cases. If the syringe breaks, it may cause the leakage of the medication. If the medication is irritating or toxic, it can cause damage to the patient's skin and tissues.
If the plastic components implanted in the body experience wear and aging due to performance degradation, they may produce tiny plastic particles. These particles may cause local inflammatory reactions and even damage surrounding tissues and organs as they travel within the body. In addition, component failure caused by performance degradation may require surgical replacement, causing both physical and psychological pain to patients.
(2) Medical operation risk
Medical plastic products with performance degradation will increase the difficulty and risk of medical operations. For example, brittle syringes are prone to breakage during the extraction of medication, which may require medical staff to replace the syringe. This not only affects operational efficiency but may also delay patient treatment. The hardening and brittleness of infusion tubes can easily lead to loose interfaces when connecting infusion devices, resulting in drug leakage and affecting the accuracy of infusion speed and dosage.
If the plastic components of surgical instruments experience a decrease in strength or fracture, it may cause functional failure of the instruments during the surgical process, affecting the normal progress of the surgery. For example, if plastic hemostatic forceps break during the hemostasis process, it may lead to uncontrollable bleeding and pose great risks to the surgery.
(3) Cross infection risk
Reusing medical plastic products that should be disposable is one of the important reasons for cross infection. Disposable syringes, infusion sets, and other products are designed with only single use safety in mind. Multiple uses can lead to the proliferation of microorganisms on the surface of the product and make it difficult to thoroughly disinfect. When these contaminated products are reused for other patients, it is highly likely to cause the spread of pathogens and trigger cross infection.
Even reusable medical plastic products can become a breeding ground for microorganisms and increase the risk of cross infection if their performance deteriorates during use, leading to surface cracks, damage, and other issues. For example, cracks on the surface of plastic trays may contain residual contaminants such as blood and body fluids, and incomplete disinfection can lead to contamination of subsequent equipment used.














